Our Commitment to Evidence-Based Formulations
Scientific Research at KYGENESIS®
At KYGENESIS®, we believe the best approach to long-term kidney and metabolic health is one rooted in evidence. Each of our ingredients has been carefully selected based on clinical studies, institutional publications, or long-standing traditional use backed by modern science. While our formulas are not intended to diagnose, treat, or cure disease, they are designed to support your body with real, researched benefits.
Clinical and In Vivo Research
These ingredients have been studied and shown to support kidney function, filtration, blood sugar, inflammation, and cardiovascular health.

- IngredientBenefit AreaKey Findings
- Astragalus RootKidney
Improved GFR and reduced proteinuria in CKD patientsYu et al., 2023 – PubMed
- Dan Shen (Salvia miltiorrhiza)Kidney
Reduced protein leakage and improved renal blood flowWang et al., 2012 – PubMed
- Magnesium CitrateKidney, Cardiovascular
Reduced vascular calcification and inflammation in CKDMassy & Drüeke, 2012 – PubMed
- Zinc CitrateKidney, Immunity
Improved antioxidant defense and lower mortality risk in dialysisCastiglioni et al., 2021 – PubMed
- Cordyceps MushroomKidney, Metabolism
Lowered creatinine/BUN and improved energy metabolismSakaguchi et al., 2019 – PubMed
- Gymnema Leaf ExtractMetabolic
Slower progression of CKD in patientsVaidya & Vassalotti, 2023 – NCBI Bookshelf
- Chromium PicolinateMetabolic
Improved insulin sensitivity and lipid markersWang et al., 2004 – PubMed
- Banaba Leaf ExtractMetabolic
Lowered fasting glucose and improved insulin responseMiura et al., 2012 – PubMed
- TaurineCardiovascular
Reduced BP and supported kidney cell membrane stabilityQaradakhi et al., 2020 – PubMed
- Vitamin C (Calcium Ascorbate)Antioxidant, Kidney
Improved oxidative balance and reduced CKD mortality riskWang et al., 2024 – PubMed
In Vitro and Mechanism-Based Studies
These ingredients are supported by laboratory or mechanistic research showing antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, or metabolic effects relevant to kidney and systemic wellness.

- IngredientBenefit AreaKey Findings
- CherryPURE® Tart CherryAntioxidant, Uric Acid
Lowered serum uric acid and CRP in human and lab studiesLamb et al., 2020 – PubMed
- Fo-Ti (Polygonum multiflorum)Anti-fibrotic, Antioxidant
TSG from Fo-Ti reduced fibrosis and oxidative stress in diabetic kidneysBounda & Feng, 2015 – PubMed
- Rehmannia RootAnti-inflammatory
Suppressed collagen buildup and TGF-β in CKD rat modelZhu et al., 2024
- Schisandra BerryAdaptogen, Antioxidant
Improved mitochondrial defense in renal oxidative stressKopustinskiene et al., 2021 – Antioxidants (Basel)
- Stinging Nettle LeafDiuretic, Anti-inflammatory
Increased urine output and improved glucose in T2DMSamakar et al., 2022 PubMed
- Parsley LeafDiuretic
Reduced oxalate crystals and improved urinary pHAl-Yousofy et al., 2017 – Am J Clin Exp Urol PubMed
- Codonopsis RootAnti-fatigue, Glucose Support
Improved metabolism and antioxidant status in nephropathy modelsChen et al., 2013 PubMed
- Cinnamon Bark ExtractBlood Sugar Control
Reduced fasting glucose and LDL in diabetic patientsAnderson et al., 2015 PubMed
- InositolInsulin Signaling
Increased insulin sensitivity and lowered HOMA-IRDiNicolantonio & O’Keefe, 2022 PubMed
- LavenderAnxiety, stress-related symptoms
Supported comfort and relaxationDonelli et al., Phytomedicine, 2019
- Couch GrassKidney
Significantly reducing serum BUN, creatinine, urea, and cystatin C levelsÇibuk et al., 2022
- MarshmallowKidney / Urinary Tract Support
Soothing urinary tissue and promoting healthy urine flow.Ahmed et al., 2023
Meet the experts behind the best kidney healing method.
Our team of experienced naturopaths and health professionals brings decades of clinical knowledge, compassionate care, and a shared mission: to empower people with kidney disease to heal naturally and avoid dialysis. With backgrounds in naturopathy, nutrition, functional medicine, education, and herbal therapy, these are the trusted experts behind our science-backed solutions and KYGENESIS® supplements—supporting you at every step of your kidney health journey.

Fiona Chin, ND
Co-Founder of Kidney Coach, B.Hsc Naturopathy, Author, Podcaster & Naturopath
Fiona is a Kidney Coach lead writer and fully qualified Naturopath with a Bachelor’s degree in health science. She has been in clinical practice for over 20 years, working in the USA, Canada and Australia.
She specializes in those diagnosed with neurological autoimmune conditions, longevity medicine, and chronic kidney disease. She co-founded Kidney Coach, which provides programs and education to empower those diagnosed with CKD, and KYGENESIS®, a supplement range designed for those diagnosed with kidney disease. She also hosts a podcast on YouTube called The Kidney Coach, a health channel dedicated to supporting those with all types of CKD.
Fiona was Australia’s first qualified Wahls practitioner, which uses scientifically proven dietary interventions to improve the outcomes for those diagnosed with autoimmune conditions. She has also undertaken post-graduate training in peptide therapy. She was also asked to be the lead author of a Springer Nature medical text on “Integrative Strategies for Those Diagnosed with Kidney Disease”, which is currently with the editors before printing in late 2025. She was also a key presenter at the Post-Viral Symposium for Long-Haul Covid in late 2024.
She worked alongside world-renowned neuroscientists and researchers when she worked for Dr. Joe Dispenza, who is rewriting the science around what is possible with meditation, the human mind and the body’s ability to heal.
When Fiona isn’t running KYGENESIS® and Kidney Coach, seeing patients, or recording podcasts, you will probably find her researching the latest breakthroughs in treatment for CKD, spinal cord injuries or other complex chronic conditions. If she isn’t doing that, she will be playing with her Dobermann Apollo.

Duncan Capicchiano, ND
Co-Founder of Kidney Coach, Naturopath, Researcher, and Author
Duncan is a second-generation Naturopath and fully qualified Nutritionist with over 20 years of experience in the health industry. He has worked across Australia and the United States, and is recognised as a leading kidney disease specialist. He developed the world’s first naturopathic kidney health program and is a best-selling author in the field.
Duncan is the co-founder of Kidney Coach, where he’s committed to making holistic kidney care accessible, practical, and empowering for people at every stage of their journey. With a background in advanced naturopathic medicine and clinical nutrition, he specialises in supporting those with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and related metabolic conditions.
Drawing on both traditional naturopathy and modern, evidence-based strategies, Duncan has helped thousands around the world improve their health and quality of life. In addition to his kidney work, he has developed respected programs for thyroid and liver health and is the author of several health-focused books.
Known for his clear, down-to-earth communication style, Duncan excels at turning complex health concepts into real-world strategies. His mission is to give people the knowledge and confidence to take control of their kidney health through natural therapies, sustainable lifestyle changes, and ongoing support.
Outside of his professional life, Duncan enjoys traveling, hiking in nature, live music, and the occasional comedy night. He’s continually exploring the latest in nutrition and functional medicine, driven by a passion to create meaningful, lasting change, one kidney at a time.

Rachel Marley ND
Qualified Naturopath & Nutritionist, BSc (Science & Education), BHSc (Naturopathy)
Rachel is a degree-qualified Naturopath and Nutritionist with almost a decade of clinical experience specialising in kidney health, gut function, immune support, children's wellbeing, and emotional health.
As a certified MINDD practitioner and FITGENES trained professional, she brings an evidence-based approach to her practice while honouring traditional naturopathic principles. Outside of clinical practice, Rachel serves as the secretary of the General Council and Register of Naturopaths, the oldest Naturopathic organisation in the UK. Rachel is passionate about collaborating with colleagues, furthering the advancement of naturopathic medicine.
At the core of Rachel's practice is a wellness-centred model of healthcare that shifts away from conventional sick-care management. She understands that very few people are living at their optimum level of wellness, with many suffering from commonplace health conditions such as fatigue, depression, and allergies. Rachel believes these conditions should not be accepted as inevitable aspects of being human but rather as signs of a body living out of balance. She has come to understand that many health challenges stem from our disconnection from our bodies and our innate state of balance.
Her expertise lies in identifying the root causes underlying health concerns, with particular emphasis on the profound connection between emotional and physical wellbeing. This understanding informs her personalised treatment protocols, which combine nutritional science, lifestyle medicine, and natural remedies tailored to each individual.
"I believe that our bodies have an innate capacity to heal when given the right conditions," Rachel explains. "My role is to help identify the obstacles to healing and provide the tools for sustainable wellness."
One of Rachel’s true passions is being a mother to her three children and three fur babies (dogs). She enjoys the peace of being in nature and loves nothing better than a walk in the woods.
A forever student at heart, she continuously expands her knowledge of the intricate relationship between physical health and emotional wellbeing through ongoing education and research. Rachel works collaboratively with patients to develop practical health strategies that honour their unique circumstances and goals, empowering them with the knowledge and support needed for their health and wellbeing journey.

Emily Cahill, ND
Naturopath & Registered Nurse – BHSc (Naturopathy), BHSc (Nursing)
With qualifications in both Naturopathy and Nursing, I bring a unique perspective to health and healing — one that bridges the gap between conventional medicine and holistic care. After completing my nursing degree in 2005 and working in an acute care hospital, I began to realise that while we were treating disease, we often weren’t getting to the root cause of it. That realisation led me to study naturopathy and embrace a more integrated, person-centred approach to health.
At KidneyCoach I work behind the scenes in customer service — supporting our community by answering emails, assisting with supplement inquiries, and helping people feel informed, heard, and confident in their next steps. It’s a privilege to be part of a company that empowers individuals to take control of their kidney health through education, natural therapies, and practical tools.
In addition to my clinical training, I’m also a Reiki and EFT practitioner and have a deep interest in the mind-body connection — how our thoughts, emotions, and beliefs can influence our physical health. I believe healing involves the whole person, not just the diagnosis, and that even small shifts in thinking can create powerful changes in wellbeing.

Stephanie MoDavis
Certified Holistic Health Provider & Yoga Therapist, Kidney Coach Peer Support Guide
Stephanie, a compassionate holistic health coach, has navigated a profound journey of healing and transformation. Her path has been marked by significant challenges, including childhood adversities (ACEs), an eating disorder, autoimmune complications, kidney failure necessitating years of dialysis, and the emotional turbulence of heartbreak and a failed relationship. Her resilience was further tested by declining health and two organ transplants. At her lowest point, Stephanie even experienced a near-death event that reshaped her perspective on life.
Stephanie's focus is to initiate and hold space for self healing and inner transformation. She has spent over 25 years in the dual role of healing practitioner, (as a yogi and naturopath), and experiencer as a patient. Her awakening occurred in 2006 and amplified exponentially in 2015.
She knows fully the consequences of living in fear and unconscious mental patterns. She has learned to walk between worlds of eastern and western traditions while advocating for holistic interrelating, self healing and modern implementation process in the West. She has experienced and acknowledges her spiritual awakening and integration process were as if not more challenging than years in kidney failure and living on dialysis. She embodies what it takes to alchemize our mental shadows while facing complexity, while holding space for our true nature to compassionately emerge.
In her personal work, she introduces and guides organizing principles related to coincidentia oppositorum." This was an important principle in Platonic philosophy and metaphysics. The union of opposing inner forces via tailored processes such as hemi-sync, initiation and trauma integration, seeing and guiding to break complex mental patterns, polarity mentorship, relationship evolution, and the spiritualization process into our new era of conscious awareness that's rooted in a healthy self aware mind and regenerated heart.
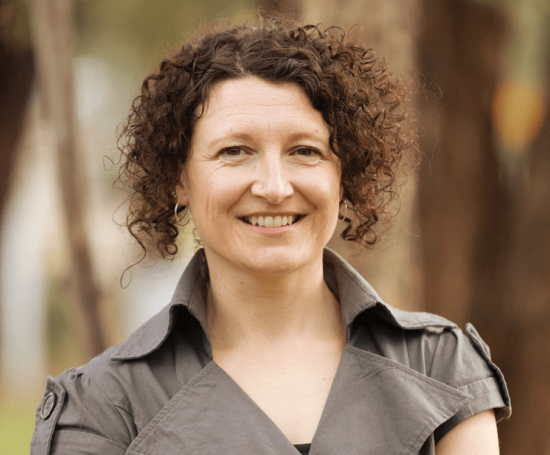

Libby Shaw, ND
Supporting wellbeing through traditional natural medicine.
Libby Shaw has over 20 years’ experience working and consulting in the natural health industry. After graduating Melbourne College of Natural Medicine (Endeavour College) in 1999, she has continued working and being mentored within a multi-disciplinary clinic in Eltham, where she gained invaluable experience in supporting individuals through their health journey.
B.HSc (Naturopathy), Ad. Dip Health Science (Naturopathy), Dip. Western Herbal Medicine, Dip. Nutrition, Ayurveda, Dip Remedial Massage, Cert. Homotoxicology, Reiki 1 & 2.
Treating clientele in areas of natural family healthcare, Libby has developed many areas of speciality including immune related conditions, thyroid conditions, digestive complaints/ food intolerances, children’s health, female reproductive conditions and healthy weight management and now kidney disease.
Libby’s caring and results focused care aims to get to the bottom of your health concerns as simply and naturally as possible without judgement. She combines a balanced approach of naturopathy, homeopathy and food as medicine to assist the body’s natural healing ability and sustainable lifestyle results.
Libby is a passionate mother of two energetic boys, gardener, food creator and student and I am constantly inspired by nature.

Dr. Matthew Lyon CD
Chiropractic and Kinesiology, practitioner of natural healing and wellness.
Dr. Matt is a U.S based chiropractor and acupuncture practitioner who owned and operated one of the largest chiropractic clinics of its kind in the world. His clinic had a 6-9 month waiting list where clients flew from around the world to participate in a wholly unique MindBody paradigm and practice of healing and wellness. He skillfully combined his mastery of energy medicine, functional medicine, coaching, and chiropractic to help people turn their lives around, regain their health, and re-experience the extraordinary.
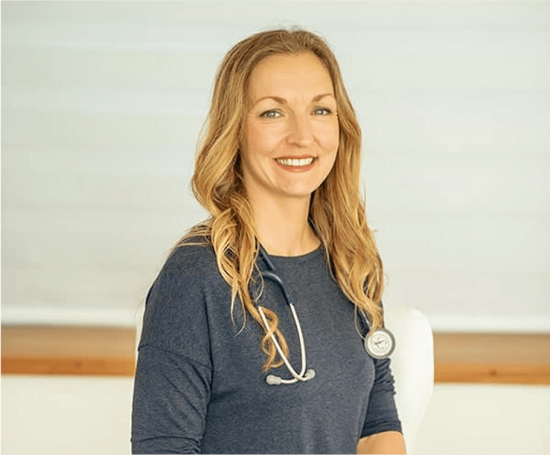

Dr. Carla Stanton MD
Family physician and certified functional medicine doctor.
Dr Carla Stanton is a GP and Functional Medicine Doctor from the UK with over two decades of clinical experience, and a former clinical teaching fellow at Nottingham University Medical School.
In more recent years she has trained in the USA in meditation and with the Institute of Functional Medicine (IFM), and in 2019 became the Medical Director of HeartMath UK; a scientifically validated biofeedback tool for increasing resilience and reducing stress.
Dr Carla now delivers performance and wellbeing programs to healthcare professionals helping to implement cultural shifts in medical establishments, travels internationally facilitating HRV (Heart Rate Variability) research with Dr Joe Dispenza, and is part of the Kidney Coach Research Team.
Comprehensive Research Summary:
Kidney-Related Clinical Studies
Alehagen, U.; Aaseth, J.; Larsson, A.; Alexander, J. - Cells 2022, 11, 509.
Decreased Concentration of Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF-23) as a Result of Supplementation with Selenium and Coenzyme Q10
This sub-analysis investigated the effects of selenium and CoQ10 on FGF-23 levels, a biomarker associated with cardiovascular health and CKD outcomes in elderly individuals.
Read PaperBi X, Yang K, Zhang B, Zhao J. - Kidney Dis (Basel). 2020 Nov;6(6):395-406.
The Protective Role of Klotho in CKD-Associated Cardiovascular Disease
Klotho protein protects against vascular calcification and heart remodeling, supporting its therapeutic relevance in CKD-related cardiovascular disease.
Read PaperBuchanan S, Combet E, Stenvinkel P, Shiels PG - Front. Endocrinol. 11:560. 2020.
Klotho, Aging, and the Failing Kidney
This review describes how reduced Klotho expression accelerates renal aging, contributing to the progression of CKD.
Read PaperChen J, Siriki R - Am J Nephrol 2015;42:318-319.
Antioxidants Therapy for Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Question of Balance
The commentary highlights the need for balanced antioxidant therapy in CKD patients, due to potential interactions and dosage concerns.
Read PaperChen K, Wang S, Sun QW, et al. - Circ Res. 2021;128(4):492-507.
Klotho Deficiency Causes Heart Aging via Impairing the Nrf2-GR Pathway
Klotho deficiency impairs antioxidant signaling pathways, leading to cardiac aging, a common comorbidity in CKD.
Read PaperDaenen K, et al. - Pediatr Nephrol. 2019;34(6):975-991.
Oxidative Stress in Chronic Kidney Disease
Oxidative stress plays a central role in CKD pathophysiology, affecting progression and complications like anemia and cardiovascular disease.
Read PaperDennis JM, Witting PK - Nutrients. 2017;9(7):718.
Protective Role for Antioxidants in Acute Kidney Disease
Summarizes evidence for antioxidants as protective agents in acute kidney injury, with possible relevance to chronic conditions.
Read PaperEugenio‐Pérez D, et al. - IntechOpen. 2016.
Role of Dietary Antioxidant Agents in Chronic Kidney Disease
Outlines how natural antioxidants in food can reduce oxidative damage in CKD, supporting integrative dietary interventions.
Read PaperHan C, Jiang YH, et al. - J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;269:113768.
Astragalus membranaceus and Salvia miltiorrhiza Ameliorate Cyclosporin A-Induced Chronic Nephrotoxicity
These herbs protect renal tissue through gut-kidney axis modulation, offering promise for reducing nephrotoxic drug side effects.
Read PaperHuang K-C, Su Y-C, Sun M-F, Huang S-T - Front. Pharmacol. 2018;9:1117.
Chinese Herbal Medicine Improves Long-Term Survival in CKD Patients
Population-based study shows that traditional herbal medicine can enhance survival outcomes when integrated with CKD care.
Read PaperJun M, Venkataraman V, et al. - Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;10:CD008176.
Antioxidants for Chronic Kidney Disease
This Cochrane review evaluates antioxidant supplements in CKD patients, showing limited but promising evidence in slowing progression.
Read PaperJurado-Fasoli L, Castillo MJ, Amaro-Gahete FJ - Nutrients. 2020;12(2):281.
Dietary Inflammatory Index and S-Klotho Plasma Levels in Middle-Aged Adults
Higher dietary inflammation scores correlate with lower Klotho levels, emphasizing the importance of an anti-inflammatory diet in aging and CKD.
Read PaperLai Q, Wei J, et al. - Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015;9:4997-5018.
Pharmacokinetic and Nephroprotective Benefits of Schisandra chinensis Extracts
Schisandra chinensis mitigates cyclosporine-induced nephrotoxicity, offering support for its use in immune-compromised CKD patients.
Read PaperL Gupta K, Sahni N - J Nephropathol. 2012;1(3):134-42.
Dietary Antioxidants and Oxidative Stress in Predialysis CKD Patients
This observational study links low intake of dietary antioxidants to elevated oxidative stress markers in CKD stages 1–4.
Read PaperLim SW, et al. - Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(15):5548–5569.
Ginseng Increases Klotho Expression via FoxO3 Pathway
In a tacrolimus-induced renal injury model, ginseng activated Klotho expression, enhancing kidney resilience to damage.
Read PaperLing XC, Kuo KL - Ren Replace Ther. 2018;4:53.
Oxidative Stress in Chronic Kidney Disease
Oxidative stress drives inflammation, fibrosis, and progression in CKD. The review advocates antioxidants as complementary therapy.
Read PaperLiu W, Gao Y, et al. - Front. Pharmacol. 2022.
Mechanism of Cordyceps sinensis in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Cordyceps sinensis is shown to modulate key diabetic and inflammatory pathways, making it a candidate for diabetic nephropathy treatment.
Read PaperLobo V, Patil A, Phatak A, Chandra N - Pharmacogn Rev. 2010;4(8):118–26.
Free Radicals, Antioxidants and Functional Foods: Impact on Human Health
This review outlines antioxidant roles in reducing oxidative stress, a common contributor to CKD and other chronic illnesses.
Read PaperLuo K, Yu JH, et al. - Sci Rep. 2019;9:7995.
Therapeutic Potential of Coenzyme Q10 in Mitochondrial Dysfunction
CoQ10 improves mitochondrial function and cellular health in tacrolimus-injured pancreatic beta cells, with renal implications.
Read PaperMinamizaki T, Konishi Y, et al. - J Endocrinol. 2018;237(3):285–300.
Soluble Klotho Causes Hypomineralization in Klotho-Deficient Mice
Study reveals paradoxical effects of soluble Klotho on bone mineralization, relevant for CKD patients at risk of bone disorders.
Read PaperOstojic SM, Engeset D - Front. Nutr. 2021;8:795599.
Improving Brain Creatine Uptake by Klotho Protein Stimulation
The review discusses Klotho’s potential to improve brain creatine uptake, with implications for anti-aging and neuroprotection in CKD.
Read PaperPiao SG, Kang SH, et al. - Transplantation. 2013;96(2):146-153.
Influence of N-acetylcysteine on Klotho in Chronic Cyclosporine Nephropathy
NAC upregulates Klotho expression and reduces oxidative stress in nephrotoxicity models, supporting its adjunctive use in CKD.
Read PaperPodkowińska A, Formanowicz D - Antioxidants. 2020;9:752.
Chronic Kidney Disease as Oxidative Stress- and Inflammatory-Mediated Cardiovascular Disease
This article describes CKD as both a cardiovascular and oxidative/inflammatory condition, promoting a broader treatment paradigm.
Read PaperPrud’homme GJ, Kurt M, Wang Q - Front. Aging. 2022;3:931331.
Pathobiology of the Klotho Antiaging Protein and Therapeutic Considerations
A detailed look at Klotho’s multifaceted role in aging and chronic disease, supporting it as a drug target in kidney and vascular health.
Read PaperRapa SF, Di Iorio BR, et al. - Int J Mol Sci. 2019;21(1):263.
Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in CKD: Therapeutic Role of Minerals, Vitamins, and Plants
Presents evidence on how specific vitamins, minerals, and plant-derived compounds can mitigate CKD-related oxidative stress.
Read PaperShen CY, Jiang JG, et al. - Br J Pharmacol. 2017;174:1395–1425.
Anti-aging Ingredients from Herbs and Nutraceuticals
Analyzes anti-aging mechanisms of herbal compounds and how they might contribute to kidney and systemic longevity.
Read PaperShibu MA, Lin YJ, et al. - Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;146:112427.
Jing Si Herbal Formula Displays Anti-Aging Effects
Jing Si, a traditional herbal blend, shows protective benefits in aging-related disorders, potentially relevant to renal aging.
Read PaperTypiak M, Piwkowska A - Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(2):956.
Antiinflammatory Actions of Klotho in Diabetic Nephropathy
Explores Klotho’s role in reducing renal inflammation and fibrosis in diabetic patients, advocating for its therapeutic activation.
Read PaperYang XH, Zhang BL, et al. - Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020; Article ID 6092715.
EGCG Reverses Klotho Hypermethylation in Diabetic Mice
EGCG, from green tea, restores Klotho gene activity and improves renal outcomes in diabetic nephropathy models.
Read PaperYu JH, Lim SW, et al. - FASEB J. 2019;33(11):12288-12298.
Coenzyme Q10 Alleviates Tacrolimus-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction
CoQ10 improves mitochondrial health in tacrolimus-injured kidney tissue, supporting its role in nephroprotective protocols.
Read PaperZhang N, Ma X, et al. - Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:914157.
Cordyceps sinensis Improves Diabetic Kidney Disease via Inhibition of TGF-β1/Smad Pathway
Cordyceps sinensis reduces renal fibrosis and inflammation in diabetic kidney disease models by modulating the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway.
Read Paper
Cart
Looks like there's nothing in your cart.
Complete your routine
-
 Kidney Diabetes Support
Kidney Diabetes SupportKidney + Metabolic Protocol
Only $172.00 USD — or Only$172.00 USDOriginal price was: $172.00 USD.$129.00 USDCurrent price is: $129.00 USD. / month $172.00 USD / one time purchase $129.00 USD / with subscription Save $43.00 USD25% OFF -
 Advanced Kidney Defense
Advanced Kidney DefenseKidney Repair Protocol 4-5
Only $182.00 USD — or Only$182.00 USDOriginal price was: $182.00 USD.$136.50 USDCurrent price is: $136.50 USD. / month $182.00 USD / one time purchase $136.50 USD / with subscription Save $45.50 USD25% OFF -
 Advanced Kidney Defense
Advanced Kidney DefenseKidney Repair Protocol 1-3
Only $182.00 USD — or Only$182.00 USDOriginal price was: $182.00 USD.$136.50 USDCurrent price is: $136.50 USD. / month $182.00 USD / one time purchase $136.50 USD / with subscription Save $45.50 USD25% OFF -
 Vital Function Defense
Vital Function DefenseKidney + Cardio Protocol
Only $172.00 USD — or Only$172.00 USDOriginal price was: $172.00 USD.$129.00 USDCurrent price is: $129.00 USD. / month $172.00 USD / one time purchase $129.00 USD / with subscription Save $43.00 USD25% OFF -
 Core Kidney Detox
Core Kidney DetoxKidney Essential Protocol
Only $172.00 USD — or Only$172.00 USDOriginal price was: $172.00 USD.$129.00 USDCurrent price is: $129.00 USD. / month $172.00 USD / one time purchase $129.00 USD / with subscription Save $43.00 USD25% OFF -
 Daily Foundational Support
Daily Foundational SupportKidney Support Protocol
Only $139.00 USD — or Only$139.00 USDOriginal price was: $139.00 USD.$104.25 USDCurrent price is: $104.25 USD. / month $139.00 USD / one time purchase $104.25 USD / with subscription Save $34.75 USD25% OFF -
 Herbal Nourishment
Herbal NourishmentNanna’s Kidney Tea
Only $39.00 USD — or Only$39.00 USDOriginal price was: $39.00 USD.$29.25 USDCurrent price is: $29.25 USD. / month $39.00 USD / one time purchase $29.25 USD / with subscription Save $9.75 USD25% OFF -
 Heart Support
Heart SupportCardio Restore™
Only $39.00 USD — or Only$39.00 USDOriginal price was: $39.00 USD.$27.30 USDCurrent price is: $27.30 USD. / month $39.00 USD / one time purchase $27.30 USD / with subscription Save $9.75 USD25% OFF -
 Glucose Balance
Glucose BalanceGluco Restore™
Only $39.00 USD — or Only$39.00 USDOriginal price was: $39.00 USD.$29.25 USDCurrent price is: $29.25 USD. / month $39.00 USD / one time purchase $29.25 USD / with subscription Save $9.75 USD25% OFF -
 Cellular Support
Cellular SupportKidney Prime®
Only $59.00 USD — or Only$59.00 USDOriginal price was: $59.00 USD.$44.25 USDCurrent price is: $44.25 USD. / month $59.00 USD / one time purchase $44.25 USD / with subscription Save $14.75 USD25% OFF -
 Filtration Protection
Filtration ProtectionKidney Advance®
Only $87.00 USD — or Only$87.00 USDOriginal price was: $87.00 USD.$65.25 USDCurrent price is: $65.25 USD. / month $87.00 USD / one time purchase $65.25 USD / with subscription Save $21.75 USD25% OFF -
 Acid Buffering
Acid BufferingKidney Alkalizing Formula Stages 4-5
Only $49.00 USD — or Only$49.00 USDOriginal price was: $49.00 USD.$36.75 USDCurrent price is: $36.75 USD. / month $49.00 USD / one time purchase $36.75 USD / with subscription Save $12.25 USD25% OFF -
 pH Optimization
pH OptimizationKidney Alkalizing Formula Stages 1-3
Only $49.00 USD — or Only$49.00 USDOriginal price was: $49.00 USD.$36.75 USDCurrent price is: $36.75 USD. / month $49.00 USD / one time purchase $36.75 USD / with subscription Save $12.25 USD25% OFF
Subtotal: $0.00 USD
- Rated 4.6 out of 5
- Try it risk-free for 60 days